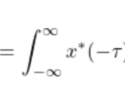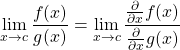Table of Contents
Introduction
The is a list of math for DSP I have found to be useful over my career in DSP. This post will be updated periodically.
More posts on DSP Math:
Cross-Correlation
Discrete-Time Cross-Correlation
(1) ![]()
Discrete-Time Autocorrelation
(2) ![]()
Fourier Transform and Inverse Fourier Transform
Transforms in frequency f (Hertz)
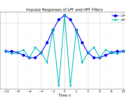
The Fourier transform relates the impulse response ![]() which is continuous in time
which is continuous in time ![]() and the frequency response X(f) which is continuous in frequency f.
and the frequency response X(f) which is continuous in frequency f.
(3) ![]()
(4) ![]()
Transforms in frequency omega (radians per second)
The Fourier transform and inverse Fourier transform can be written with the frequency f in Hertz, or by using ![]() which is in radians per second.
which is in radians per second.
(5) ![]()
(6) ![]()
Fourier transform references here.
Fourier Transform Pairs
(7) ![]()
(8) ![]()
(9) ![]()
(10) ![]()
Derivations for (8), (9) and (10) here: Fourier Transform Pairs of Conjugation and Time Reversal
Fourier Transform Properties
Convolution Property
Linearity Property
Discrete-Time Fourier Transform and Inverse Transform
The discrete-time Fourier transform relates the impulse response x[n] which is discrete in time n and the frequency response ![]() which is continuous in frequency
which is continuous in frequency ![]() .
.
(13) ![]()
(14) ![]()
Trigonometric Identities
Calculus
Integration by Parts
(18) ![]()
Derivatives
(19) ![]()
(20) ![]()